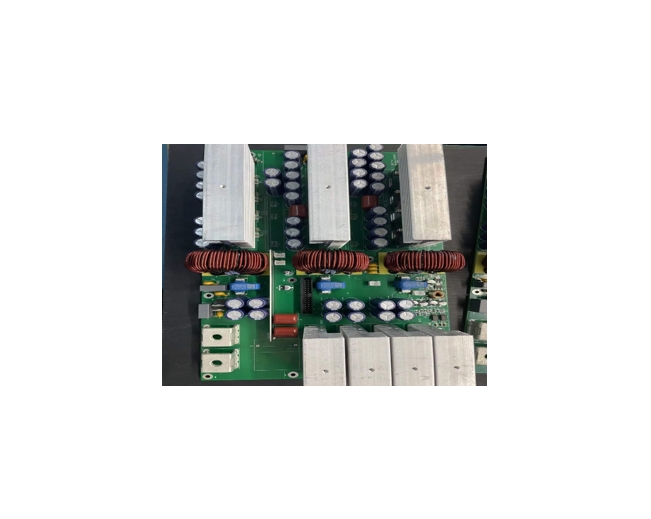
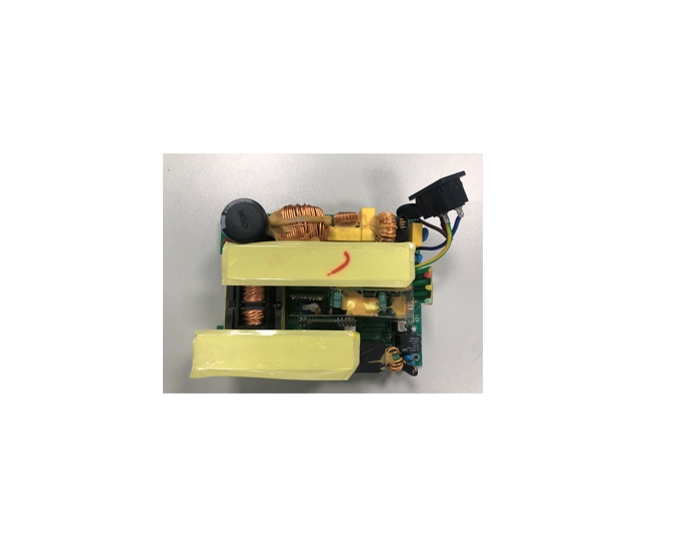
Heat dissipation is a key focus, particularly in the age of ever more powerful AI data centers, as high-power operation generates significant heat, necessitating PCB layout optimization—such as using large-area copper foil for heat conduction—and the application of advanced thermal materials such as thermal grease. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is equally important, with measures such as shielding covers and filter circuits employed to suppress high-frequency interference. To ensure energy efficiency and reliability, these PCBA must also meet high conversion efficiency standards, like the “80 Plus” certification for computer power supply units, and maintain long-term stable operation.
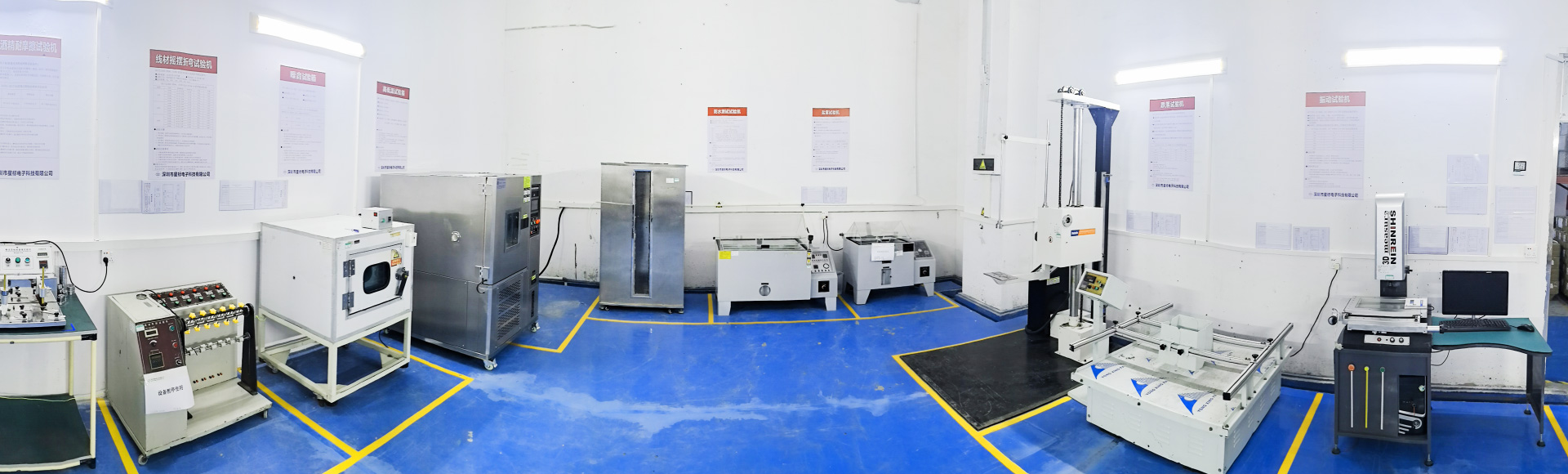
In our PCBA production, both SMT and DIP techniques are utilized; SMT enables high-precision soldering of small components such as capacitors and chips, while DIP is used for inserting larger components like transformers and heat sinks. Rigorous testing procedures, including load testing to simulate full-load operation, withstand voltage testing for safety, and burn-in testing to verify long-term stability, are also integral to the manufacturing process.